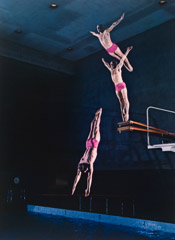Harold Edgerton
Harold Eugene “Doc” Edgerton, Sc.D. (1903-1990)
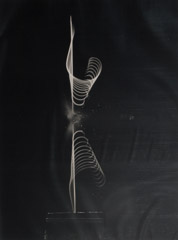
Edgerton was a professor of electrical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is largely credited with transforming the stroboscope from an obscure laboratory instrument into a common device seen in nearly every camera. He grew up in Aurora, Nebraska and attended the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. After graduating, he married Esther Garret in 1928. During their marriage they had three children: William, Robert, and Mary Lou. He earned an S.M. in electrical engineering from MIT in 1927. Edgerton used stroboscopes to study synchronous motors for his Sc.D. thesis in electrical engineering at MIT, awarded in 1931. He credited Charles Stark Draper with inspiring him to point stroboscopes at everyday objects: the first was a stream of water coming out of a faucet. He was a pioneer in strobe photography, subsequently using the technique to capture images of balloons during their bursting, or a bullet during its impact with an apple, for example. He was awarded a bronze medal by the Royal Photographic Society in 1934, and the National Medal of Science in 1973. He also invented the Rapatronic camera.
In 1937 he began a lifelong association with photographer Gjon Mili, who used stroboscopic equipment, particularly a “multiflash” strobe light, to produce strikingly beautiful photographs, many of which appeared in Life Magazine. He was a cofounder of the company EG&G, with Kenneth Germeshausen and Herbert Grier, in 1947. EG&G became a prime contractor for the Atomic Energy Commission and had a major role in photographing and recording nuclear tests for the United States through the fifties and sixties. His work was instrumental in the development of side-scan sonar technology, used to scan the sea floor for wrecks. Edgerton worked with the undersea explorer Jacques Cousteau, by first providing him with underwater stroboscopes, and then by using sonar to discover the Britannic. Edgerton participated in the discovery of the American Civil War battleship USS Monitor. While working with Cousteau, he acquired the nickname he is still known by in photographic circles, “Papa Flash”. In addition to having the scientific and engineering acumen to perfect strobe lighting commercially, Edgerton is equally recognized for his visual aesthetic: many of the striking images he created in illuminating phenomena that occurred too fast for the naked eye adorn art museums worldwide. He was especially loved by MIT students for his willingness to teach and his kindness: “The trick to education,” he said, “is to teach people in such a way that they don’t realize they’re learning until it’s too late.” One of the graduate student dormitories at MIT carries his name. Edgerton’s work was featured in an October 1987 National Geographic Magazine article entitled Doc Edgerton: the man who made time stand still.
Born: April 6, 1903, Freemont NE
Died: January 4, 1990, Cambridge, MA